MNIST using XGboost
Predicting MNIST Digits with XGBoost: A Surprisingly Effective Approach
In the world of machine learning, the MNIST dataset is a classic benchmark for image classification tasks. Typically, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are the go-to choice for such tasks. However, in this post, we'll explore a less conventional but surprisingly effective approach: using XGBoost, a gradient boosting algorithm, to classify handwritten digits.
Why XGBoost for Image Classification?
XGBoost is primarily known for its prowess in structured data tasks, but it can also be applied to image data with impressive results. The key lies in treating the pixel values as features, which allows tree-based models like XGBoost to capture complex patterns in the data.
The Code
Let's dive into the code to see how this works. We'll use Python along with popular libraries like Pandas, XGBoost, and Scikit-learn.
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, confusion_matrix, classification_report
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
# Load data
train_data = pd.read_csv('data/train.csv')
test_data = pd.read_csv('data/test.csv')
sample = pd.read_csv('data/sample_submission.csv')
# Split the training data into training and validation sets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train_split, X_val_split, y_train_split, y_val_split = train_test_split(
X_train, y_train, test_size=0.2, random_state=42
)
# Train the XGBoost classifier
clf = XGBClassifier(
objective='multi:softmax', # For multi-class classification
num_class=10, # Number of classes (digits 0-9)
random_state=42,
n_jobs=-1 # Use all CPU cores
)
clf.fit(X_train_split, y_train_split)
# Predict on the validation set
y_pred = clf.predict(X_val_split)
# Evaluate the model
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_val_split, y_pred)
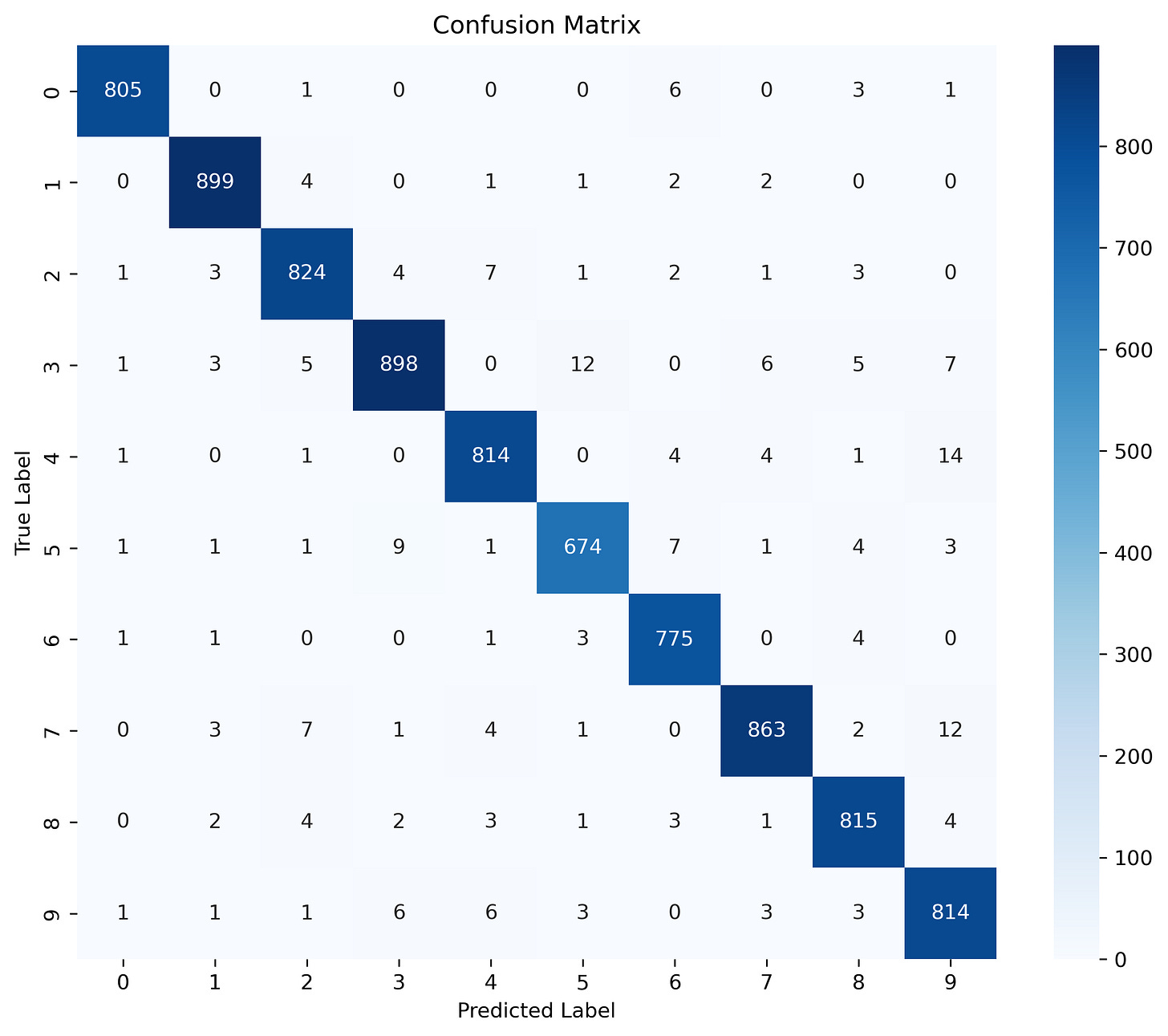
conf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_val_split, y_pred)
class_report = classification_report(y_val_split, y_pred)
print(f'Accuracy: {accuracy}')
print('Confusion Matrix:')
print(conf_matrix)
print('Classification Report:')
print(class_report)Validation Accuracy: 0.9739
Results
The results might surprise you! Despite being a tree-based model, XGBoost achieves a high accuracy on the MNIST dataset, often exceeding 97.39%. This demonstrates the versatility and power of gradient boosting algorithms, even for tasks traditionally dominated by neural networks.